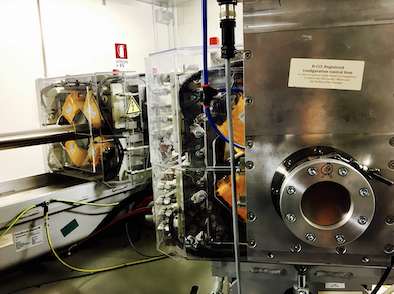
A fast and reliable system to measure transversal charged particles relative dose profiles is desirable in any hadrontherapy facility, being the basis for an accurate treatment quality assessment procedure. For this purpose, a system for the lateral dose profile reconstruction was developed at the Laboratori Nazionali del Sud of Italian Institute for Nuclear Physics (INFN-LNS, Catania, Italy);...
Three batches (A, B, C) of thermoluminescent dosimeters TLDs-100 (LiF:Mg, Ti), provided by the team of the Radioactivity Laboratory (LaRa) of Physics Department of Federico II University of Naples, were characterized to Trento Proton Beam Line. Afterwards, the TLDs have been used to obtain the dose profile in a series of radiobiological experimental activities implemented in the context of the...
The possibility to use polymer based scintillators for the detection of ionizing particles is of extreme interest in several fields, ranging from security purposes, where the revelation of neutrons and gammas is mandatory to hamper the traffic of nuclear weapons, workers radioprotection in sites as nuclear energy plants nuclear medicine laboratories and nuclear physics research facilities,...
The development of detectors for protons and heavy particles is a long-lasting research topic not only for fundamental applications, but, more recently, for monitoring energy and flow of particles in ion beam applications. However, the most demanding application of ion beams, for which accurate measurements are increasingly needed, is hadron therapy of cancer. For this application there is an...
Organic scintillators are largely exploited in a wide range of detectors due to their capability to obtain very good time resolutions. Plastic scintillators are also relatively cheap, easy to manipulate and light (low density) with respect to conventional crystal scintillators. Traditionally they are exploited to perform very precise measurements ...
Radiation therapy is the most-effective cytotoxic therapy available for the treatment of localized solid cancers. With the introduction of charged particle radiotherapy (proton therapy), the area of irradiated healthy tissue surrounding the tumor was further decreased. The aim of this study is to investigate the role of p53 in both X-rays and proton therapy treatments. p53 is a transcription...
Although three decades of research have been trialled, the prognosis for patients with high-grade gliomas (HGGs) has not significantly changed.
The aim of our project is the development of a new combined treatment that could sensitize HGGs to therapies, reducing side effects and improving quality of life of the patients.
We will develop a new multidisciplinary protocol, combining the...
In light of future human exploration of deep space, a fundamental need is to understand how terrestrial organisms may be affected by the peculiar conditions that characterize this extreme environment. Moreover, it will be crucial to dissect how the individual genetic structure may jeopardize or facilitate the adaptation to deep space, with specific regards to normal functioning of the nervous...
The radiosensitivity of biological systems is strongly affected by the system oxygenation. On the molecular level, this effect is considered to be related to the indirect damage and in particular to the effect of the OH• radicals. Several theories have been developed and among them the so called oxygen fixation hypothesis is so far the most accepted one. Recent studies open up another possible...
The SIRMIO (Small Animal Proton Irradiator for Research in Molecular Image-guided Radiation-Oncology) project [1] aims at developing a portable preclinical proton irradiator that can be installed at existing proton therapy centres. The clinical beam properties will be adapted to match requirements of small-animal irradiation using a dedicated energy degradation and focussing system [2]....
In hadron therapy a highly conformed irradiation field is delivered to the target by moving the beam and modulating its energy. Treatment plans require precisely measured patients’ Stopping Power (SP) maps, which are presently extracted from X-rays tomographies, so introducing unavoidable uncertainties. A direct measurement of the SP maps using protons (proton Computed Tomography - pCT), could...
PURPOSE
To present the GR5 project titled “XpCalib – Proton therapy X-ray CT calibration by proton tomography” recently financed by INFN.
BACKGROUND
In recent past, INFN research projects such as Prima, RDH and IRPT have studied the feasibility of proton Computed Tomography (pCT) as a tool to improve treatment accuracy in hadron therapy.
In this framework a pre-clinical prototype has...
In the last years, our group has performed different radiation physics experiments from the fields of particle therapy and space radiation protection. This contribution will summarize briefly the conducted experiments and present the obtained results.
One experiment investigated the entrance channel of proton Bragg curves. The shape of the first few centimetres of a proton depth dose profile...
LIDAL is a detector designed to study the radiation flux and energy spectra in Low Earth Orbit, it is onboard the International Space Station (ISS) since January 2020. It has been developed coupling a TOF system, based on fast plastic scintillators read by PMTs, with the ALTEA subsystem, a series of silicon detector telescopes which already operated on the ISS between 2006 and 2012 (Zaconte et...
We discuss the experimental procedure and the results of an irradiation campaign on GAGG:Ce (Cerium-doped Gadolinium Aluminium Gallium Garnet) scintillator crystals, carried out in the framework of the HERMES-TP/SP (High Energy Rapid Modular Ensemble of Satellites --- Technological and Scientific Pathfinder) mission at the Trento Proton Therapy Centre (TPTC) during January 2019. Samples from...